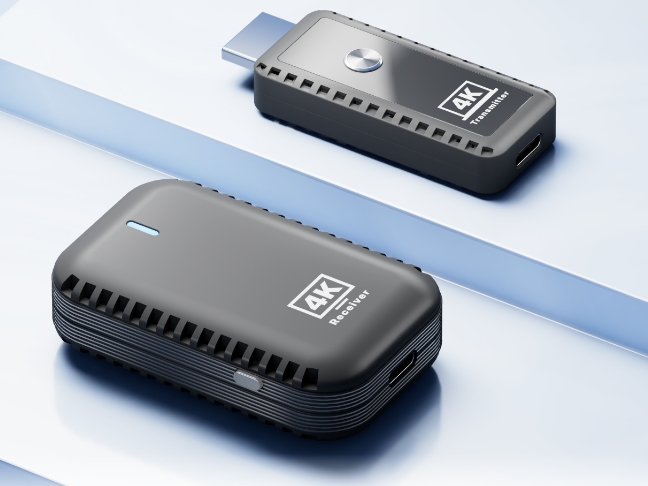
HDMI wireless transmitters are devices designed to transmit high-definition video and audio signals from one source to another without the need for physical cables. These devices are increasingly popular in home theaters, office presentations, and digital signage systems due to their convenience and flexibility. Understanding the technical specifications of HDMI wireless transmitters helps consumers make informed decisions when choosing the right device for their needs.
Resolution and Video Quality
One of the most important specifications of an HDMI wireless transmitter is the video resolution it supports. Most modern transmitters support Full HD (1080p), 4K, or even 8K resolution. For high-quality video streaming, a transmitter should support at least 1080p, with 4K being ideal for more demanding applications such as gaming or high-definition movie streaming. Higher resolution transmitters often require more bandwidth and better compression technologies to maintain signal integrity.
Wireless Standards and Frequency Bands
HDMI wireless transmitters use different wireless standards to send signals. Many devices utilize Wi-Fi (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bands), while others use radio frequency (RF) signals, particularly in the 60 GHz band. The 5 GHz Wi-Fi band offers a better balance between range and speed, while 60 GHz RF provides higher speeds and less interference but typically works over shorter distances. The specific frequency band used affects the transmission range and the quality of the signal in different environments.
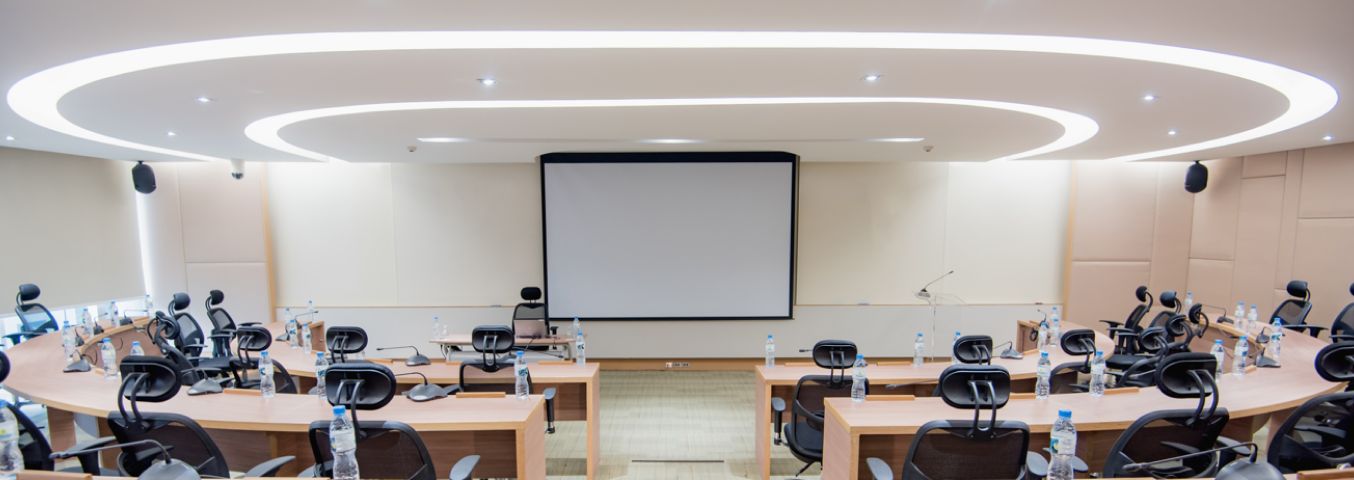
Transmission Range
The range of an HDMI wireless transmitter is another crucial parameter. Most wireless HDMI transmitters offer a range of 30 to 100 feet (10 to 30 meters) in open spaces. However, obstacles such as walls, floors, and interference from other devices can reduce this range. High-performance models may offer extended range or improved signal stability, making them suitable for larger spaces or setups with multiple obstructions.
Latency and Compression
Latency refers to the delay between the transmission and reception of the signal. In most cases, latency is measured in milliseconds (ms), and lower latency is important for activities like gaming or live presentations. A good HDMI wireless transmitter should have a latency of under 50 ms to ensure smooth video and audio synchronization. Additionally, compression algorithms play a significant role in the performance of the transmitter. Lossless compression minimizes signal degradation, while lossy compression can reduce bandwidth requirements but may lead to a slight loss in quality.
Power Supply and Connectivity
HDMI wireless transmitters usually require a power adapter to operate. Some models also feature USB-powered options for convenience. The input/output (I/O) ports typically include an HDMI input for the source device and an HDMI output for connecting to a receiver or display. Some models also come with additional ports for audio or Ethernet connections, providing more versatility.
Compatibility and Security
Most HDMI wireless transmitters are compatible with standard HDMI devices, making them easy to integrate into existing setups. Additionally, some transmitters support HDCP (High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection), ensuring the secure transmission of protected content. Encryption technologies may also be used to secure the wireless signal, especially in business or professional environments.
Conclusion
When choosing an HDMI wireless transmitter, it is essential to consider the device’s resolution support, wireless standards, range, latency, and power requirements. These technical specifications will help determine the performance and suitability of the device for different applications. By understanding these parameters, users can select a transmitter that meets their needs for high-quality, wireless video and audio transmission.