Wireless HDMI factory plays a crucial role in the evolving world of consumer electronics by providing innovative solutions for wireless high-definition video and audio transmission. As demand for wireless connectivity continues to grow, these factories focus on developing cutting-edge products that eliminate the need for cumbersome cables, offering a cleaner, more efficient way to connect devices. The wireless HDMI industry has gained significant traction in recent years, thanks to the increasing need for flexibility and convenience in home entertainment, gaming, and business environments. By producing high-performance wireless HDMI transmitters and receivers, these factories are driving the shift toward cable-free, high-quality media streaming.
What is Wireless HDMI?
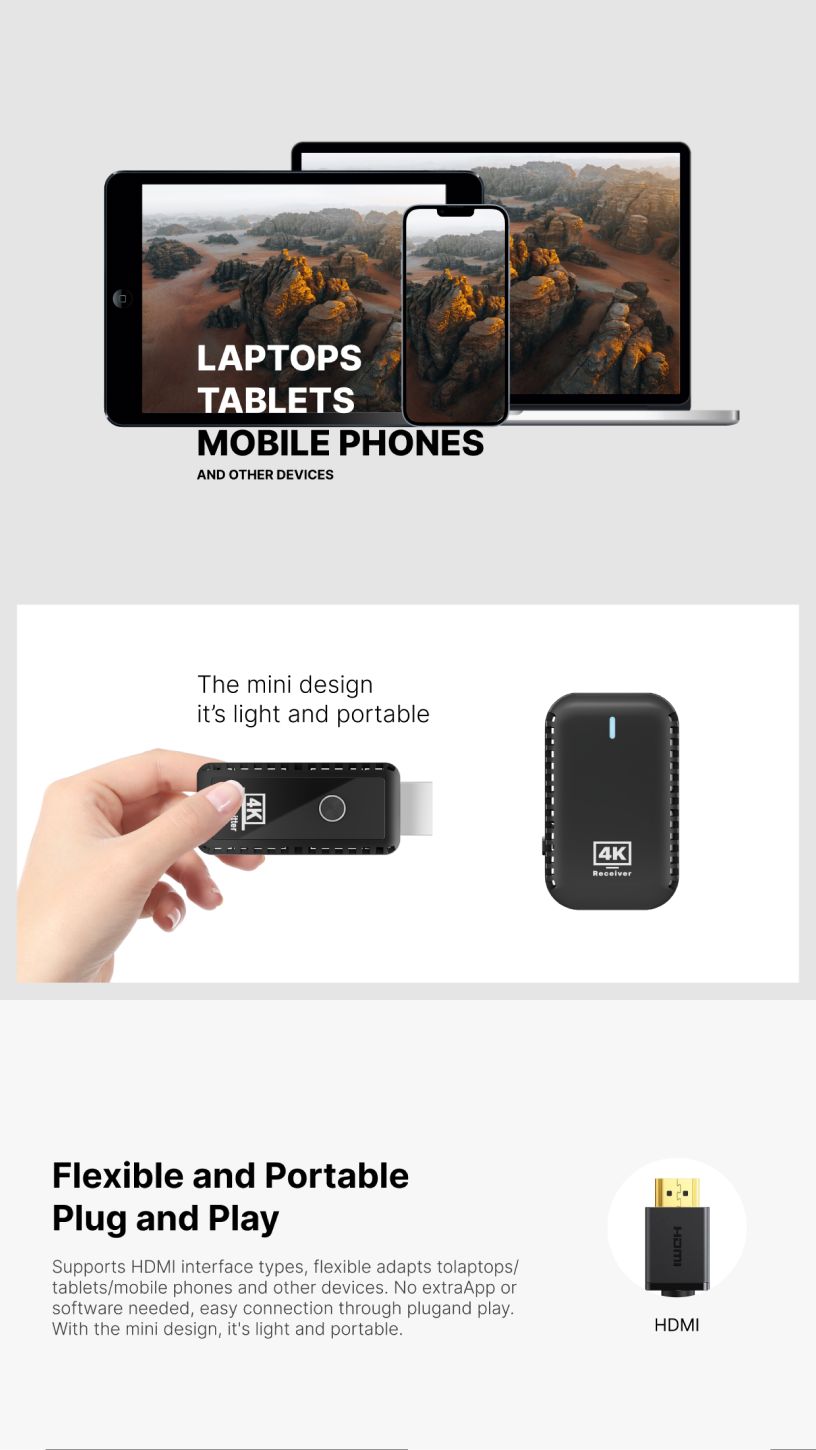
Wireless HDMI technology allows users to transmit HD video and audio signals from one device to another without the need for physical cables. It eliminates the mess of tangled wires and provides more flexibility in terms of device placement. Whether it's for home entertainment systems, office presentations, or gaming setups, wireless HDMI offers a seamless, high-quality connection without compromising performance.
The Role of Wireless HDMI Factories
A wireless HDMI factory specializes in designing, developing, and manufacturing devices that enable wireless transmission of high-definition signals. These factories often focus on creating HDMI transmitters and receivers that operate on advanced wireless technologies such as Wi-Fi or dedicated wireless standards. The goal is to produce reliable, high-performance products that can handle the increasing demand for wireless connectivity in consumer electronics.
In a typical wireless HDMI factory, research and development teams work on refining the technology to enhance the range, speed, and stability of the signal. Additionally, factories must ensure that their products comply with industry standards to guarantee compatibility across a wide range of devices, from televisions and projectors to laptops and gaming consoles.
Benefits of Wireless HDMI Technology
The most obvious advantage of wireless HDMI technology is the reduction of cables, which not only creates a cleaner and more organized space but also increases flexibility in device setup. Without wires, devices can be placed in more convenient or aesthetically pleasing locations, and users can enjoy the freedom of mobility while watching movies or playing games.
Furthermore, wireless HDMI devices support high-definition video resolutions, including 4K and even 8K, making them ideal for modern, high-performance home entertainment systems. The high-quality transmission also ensures that there is no loss of signal integrity, providing a smooth and enjoyable viewing experience.
Challenges Faced by Wireless HDMI Factories
Despite its many advantages, wireless HDMI technology is not without its challenges. One of the primary concerns for manufacturers is minimizing latency. Lag or delays in signal transmission can disrupt the viewing experience, especially in fast-paced content like gaming or sports. Ensuring minimal latency while maintaining high video quality is a delicate balancing act for wireless HDMI factories.
Another challenge is overcoming interference. Wireless signals are susceptible to disruption from other devices operating on similar frequencies, such as Wi-Fi routers and Bluetooth devices. Factories must invest in advanced technologies and robust testing to minimize signal degradation and ensure consistent performance in various environments.
Conclusion
Wireless HDMI technology is transforming the way we connect and experience multimedia content, and wireless HDMI factories are at the heart of this revolution. By continually advancing the technology and addressing the challenges of latency and interference, these factories are making it possible for consumers to enjoy a more streamlined, high-quality entertainment experience. As demand for wireless solutions continues to rise, the role of wireless HDMI factories will only become more crucial in shaping the future of electronics.